Novel Coronavirus Outbreak Nov 12 - Nov 19
Most recent articles (newest articles listed first)
Quantitative analysis of the impact of COVID‐19 on the emergency medical services system in Tokyo
Hypocalcemia and massive pulmonary embolism in SLE patient with COVID‐19 infection: A case report
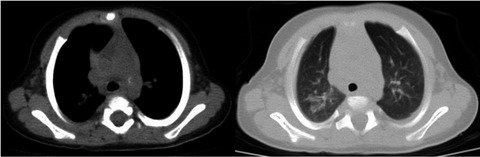
A deep and handcrafted features‐based framework for diagnosis of COVID‐19 from chest x‐ray images
Letter to the editor: “Autoimmune hepatitis after COVID‐19 vaccination”
- Hepatology
- 756-756
- 10.1002/hep.32249
The COVID‐19/racial injustice syndemic and mental health among Black Americans: The roles of general and race‐related COVID worry, cultural mistrust, and perceived discrimination
COVID‐19 vaccines mix‐and‐match: The concept, the efficacy and the doubts
- Journal of Medical Virology
- 1294-1299
- 10.1002/jmv.27463
Effects of hypertonic alkaline nasal irrigation on COVID‐19
Susceptibility of white‐tailed deer to SARS‐CoV‐2
- Veterinary Record
- 408-409
- 10.1002/vetr.1204
Some characteristics of clinical sequelae of COVID‐19 survivors from Wuhan, China: A multi‐center longitudinal study
High sleep fragmentation parallels poor subjective sleep quality during the third wave of the Covid‐19 pandemic: An actigraphic study
Impact of COVID – 19 in patients awaiting liver transplantation
- Liver International
- 256-257
- 10.1111/liv.15105
Solid non‐lung organs from COVID‐19 donors in seropositive or naive recipients: Where do we stand?
COVID‐19 vaccination timing and kidney transplant waitlist management: An international perspective
Globalisation, economic uncertainty and labour market regulations: Implications for the COVID‐19 crisis
- The World Economy
- 2165-2187
- 10.1111/twec.13230
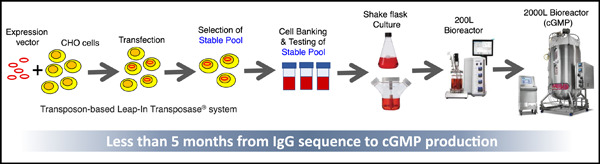
Rapid cGMP manufacturing of COVID‐19 monoclonal antibody using stable CHO cell pools
Ambivalent heroism? – Psychological burden and suicidal ideation among nurses during the Covid‐19 pandemic
- Nursing Open
- 785-800
- 10.1002/nop2.1130
Effectiveness of public policy in reviving the COVID-19 hit economy: Evidences from Kerala, India
A coarse‐refine segmentation network for COVID‐19 CT images
Impact of COVID‐19 lockdowns on registrar reporting volumes in a Melbourne teaching hospital
‘Anxiety is still ongoing!’ Evaluation of the effect of the COVID-19 pandemic on anxiety severity of physicians working in the internal medicine department after 1 year: a collaborative cross-sectional study
- Internal Medicine Journal
- 1940-1945
- 10.1111/imj.15558
Epidemiology of SARS‐CoV‐2 infection and SARS‐CoV‐2 positive hospital admissions among children in South Africa
COVID‐19 — Two years in
Heard, valued, supported? Doctors' wellbeing during transitions triggered by COVID-19
- Medical Education
- 516-526
- 10.1111/medu.14698
Invited letter: Integrated palliative care in a geriatric mental health setting during the COVID‐19 pandemic
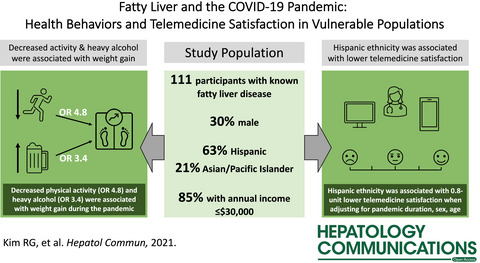
Fatty Liver and the Coronavirus Disease 2019 Pandemic: Health Behaviors, Social Factors, and Telemedicine Satisfaction in Vulnerable Populations
- Hepatology Communications
- 1045-1055
- 10.1002/hep4.1873
Clearance of Lormetazepam, Midazolam, and Their Conjugated Metabolites by Continuous Venovenous Hemofiltration During Prolonged Sedation in Critically Ill Patients With COVID‐19‐Associated Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome
Population pharmacokinetic modeling of GS‐441524, the active metabolite of remdesivir, in Japanese COVID‐19 patients with renal dysfunction
Predictors and outcomes of respiratory failure among lung transplant patients with COVID‐19
Wearable remote monitoring and COVID‐19
Impacts of the COVID pandemic on international faculty's academic activities and life in Japan
Herpes zoster duplex following COVID‐19
Adherence to systemic therapy in patients with psoriasis during the COVID‐19 pandemic: A multicenter study
Trends in cosmetic consumer preferences during COVID‐19 pandemic: Comparing 2021 to 2020
SARS Cov-2 vaccination induces de novo donor-specific HLA antibodies in a renal transplant patient on waiting list: A case report
- HLA
- 25-30
- 10.1111/tan.14492
Rapid Adoption of Telemedicine in Rheumatology Care During the COVID-19 Pandemic Highlights Training and Supervision Concerns Among Rheumatology Trainees
Zn‐Induced Interactions Between SARS‐CoV‐2 orf7a and BST2/Tetherin
- ChemistryOpen
- 1133-1141
- 10.1002/open.202100217
Graphical Abstract
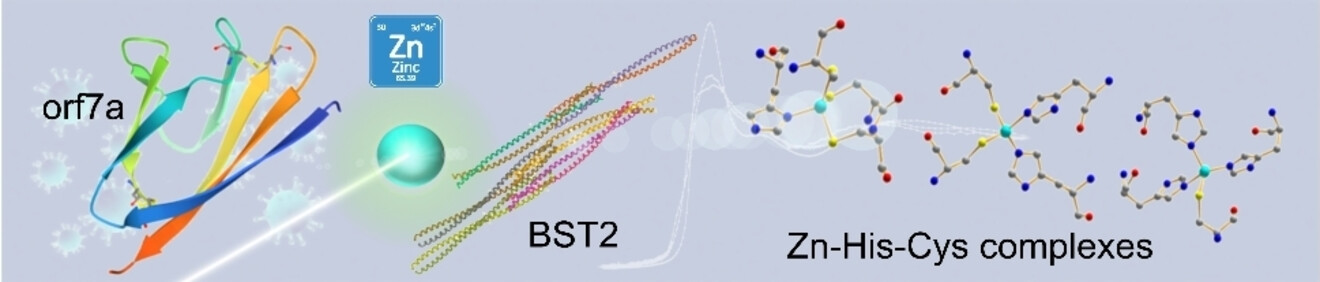
Think zinc! We conjecture that in the case of SARS-CoV-2, the orf7a accessory protein acts as a BST2 antagonist. We provide evidence, based on sequence analysis, Molecular Dynamics simulations as well as XAS experiments, that Zn ions play a key role in the SARS-CoV-2 virus strategy to escape the immune response mediated by the BST2 host protein.
mRNA vaccines against COVID‐19: a showcase for the importance of microbial biotechnology
HEALTH: Covid‐19 Round‐Up
Cutaneous and Allergic reactions due to COVID‐19 vaccinations: A review
Comparative Risk: Dread and Unknown Characteristics of the COVID‐19 Pandemic Versus COVID‐19 Vaccines
- Risk Analysis
- 2214-2230
- 10.1111/risa.13852
Strategies to aid self‐isolation and quarantine for individuals with severe and persistent mental illness during the COVID‐19 pandemic: A systematic review
Highlights
-
Individuals with severe and persistent mental illness (SPMI) have a higher risk of contracting COVID-19 than individuals without SPMI.
-
This review aimed to synthesize evidence for interventions to support self-isolation and mandated quarantine for COVID-19 among individuals with SPMIs.
-
Only one study met our inclusion criteria. This study found a beneficial effect of a dedicated isolation hotel for individuals experiencing homelessness and COVID-19—where approximately 25%–50% of the study sample had a mental or substance use disorder.
-
While there has been an abundance of COVID-19 protocols in general, information for SPMIs is lacking.
-
As the pandemic continues and we better prepare for future pandemics, developing protocols for supporting SPMIs in this context is imperative.
Rationing of a scarce life‐saving resource: Public preferences for prioritizing COVID‐19 vaccination
- Health Economics
- 342-362
- 10.1002/hec.4450
A 2-month post-COVID-19 follow-up study on patients with dyspnea
COVID-19 and renin angiotensin aldosterone system: Pathogenesis and therapy
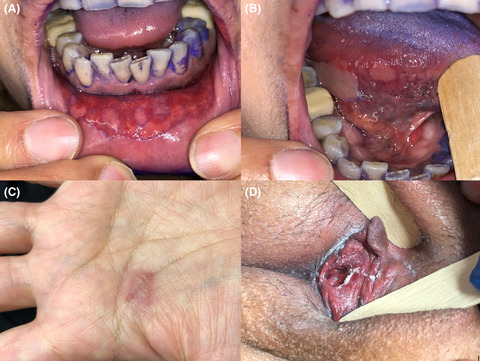
In Reference to Association of Severe Tongue Edema With Prone Positioning in Patients Intubated for COVID-19
In Response to Association of Severe Tongue Edema With Prone Positioning in Patients Intubated for COVID-19
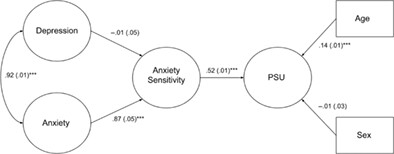
COVID‐19 pandemic‐related stressors and posttraumatic stress: The main, moderating, indirect, and mediating effects of social support
- Stress and Health
- 522-533
- 10.1002/smi.3115
Bullous pemphigoid triggered by COVID-19 vaccine: Rapid resolution with corticosteroid therapy
Effects and policies of COVID‐19
Monoclonal antibody treatment for COVID‐19 in solid organ transplant recipients
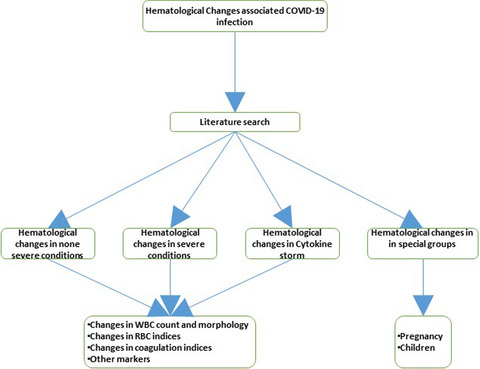
Clinical characteristics, laboratory parameters and outcomes of COVID‐19 in cancer and non‐cancer patients from a tertiary Cancer Centre in India
- Cancer Medicine
- 8777-8788
- 10.1002/cam4.4379
Graphical Abstract
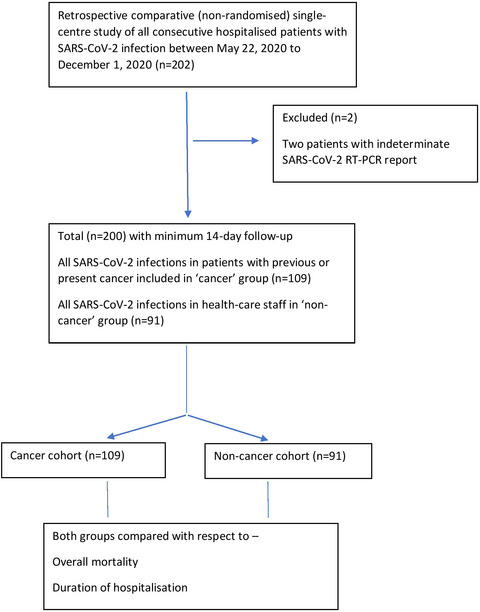
This is the first data from India, describing comparison of cancer and non-cancer patients with COVID-19 treated with a uniform protocol. It shows that cancer patients with COVID-19 have higher mortality and require longer hospital stay. High procalcitonin levels and oxygen requirement during admission are factors that adversely affect outcomes.
Impact of COVID‐19 pandemic on acute heart failure admissions and mortality: a multicentre study (COV‐HF‐SIRIO 6 study)
- ESC Heart Failure
- 721-728
- 10.1002/ehf2.13680
Applying critical realism to the COVID‐19 pandemic to improve management of future public health crises
Usefulness of SARS‐CoV‐2 antigen test sample as input for SARS‐CoV‐2 RT‐PCR analysis
- Journal of Medical Virology
- 1693-1695
- 10.1002/jmv.27459
Evaluation of human coronavirus OC43 and SARS‐COV‐2 in children with respiratory tract infection during the COVID‐19 pandemic
- Journal of Medical Virology
- 1450-1456
- 10.1002/jmv.27460
Highlights
-
The same frequency of SARS-COV-2 and HCoV-OC43 was found in children with respiratory symptoms during the COVID-19 pandemic.
-
The rate of co-infection of SARS-COV-2 with HCoV-OC43 was 0.08. The frequency of fever, headache, edema, vomiting, abdominal complaints and myalgia was significantly higher in the HCoV-OC43 group compared with the SARS-COV-2 group.
Variants of concern responsible for SARS‐CoV‐2 vaccine breakthrough infections from India
- Journal of Medical Virology
- 1696-1700
- 10.1002/jmv.27461
Functional Movement Disorders During the COVID-19 Pandemic: Back to Charcot's Era at the Salpêtrière
- Movement Disorders
- 432-434
- 10.1002/mds.28875
Acute-onset polyradiculoneuropathy after SARS-CoV2 vaccine in the West and North Midlands, United Kingdom
- Muscle & Nerve
- 233-237
- 10.1002/mus.27461
Computational Method‐Based Optimization of Carbon Nanotube Thin‐Film Immunosensor for Rapid Detection of SARS‐CoV‐2 Virus
Graphical Abstract
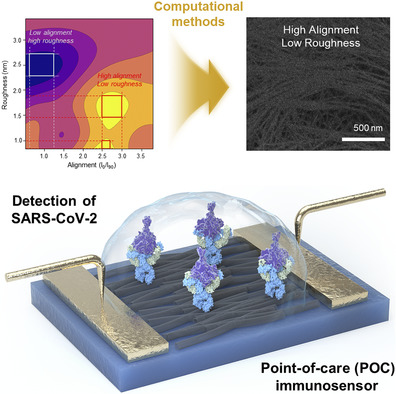
Computational method-based systematic analysis that can optimize the carbon nanotube (CNT) thin-film properties and sensitivity of immunosensors is utilized, potentially enabling mass manufacturing of point-of-care biosensor for accurate and rapid diagnosis of various diseases. Using CNT films with high alignment and low roughness, nucleocapsid protein in SARS-CoV-2 virus is detected with a sensitivity of 0.048 [copies/mL]−1.
Rhythms of the day: How electronic media and daily routines influence mood during COVID‐19 pandemic
PostCOVID effect on endothelial function in hypertensive patients: A new research opportunity
Medicare and telehealth: The impact of COVID-19 pandemic
Two years into COVID-19 – Lessons in SARS-CoV-2 and a perspective from papers in FEBS Letters
- FEBS Letters
- 2847-2853
- 10.1002/1873-3468.14226
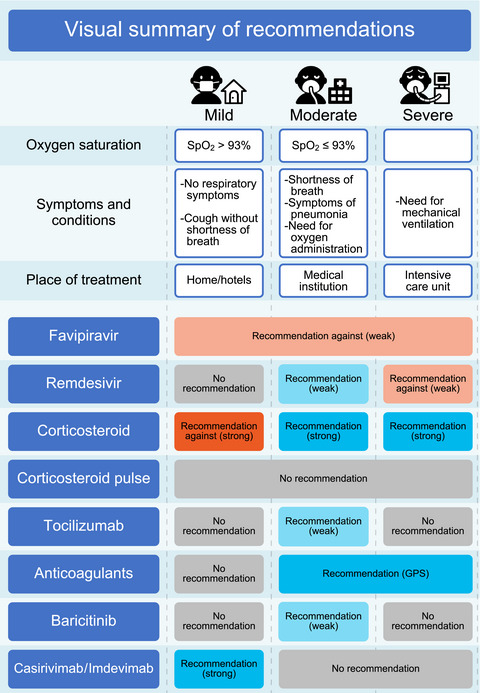
Japanese rapid/living recommendations on drug management for COVID‐19: updated guidelines (September 2021)
Reply
What lies behind and beyond acute COVID‐19 pain?
Determination of lipid content and stability in lipid nanoparticles using ultra high‐performance liquid chromatography in combination with a Corona Charged Aerosol Detector
- ELECTROPHORESIS
- 1091-1100
- 10.1002/elps.202100244
Impact of the Corona Virus Disease 2019 Pandemic on Hepatology Practice and Provider Burnout
- Hepatology Communications
- 1236-1247
- 10.1002/hep4.1870
Acquired thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura following Pfizer COVID‐19 vaccination
- eJHaem
- 207-210
- 10.1002/jha2.342
Incidence of SARS‐CoV‐2 infection among asymptomatic patients undergoing preoperative COVID testing prior to cancer surgery: ASPECT study
Animal models for SARS‐CoV‐2 infection and pathology
- MedComm
- 548-568
- 10.1002/mco2.98
Graphical Abstract
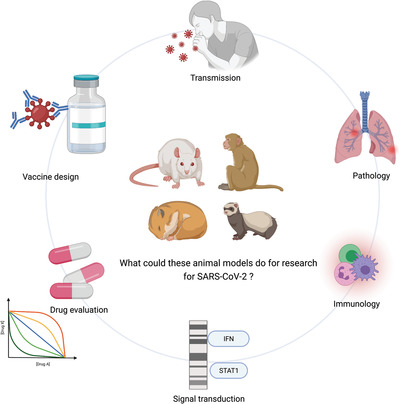
Animal models that recapitulate characteristics and immune responses observed in COVID-19 patients are urgently needed. These animal models such as mouse, hamster, nonhuman primate, and ferret, have provided robust platforms for studying the transmission, pathogenesis, and immunology induced by SARS-CoV-2, and for evaluating the immunomodulatory and antiviral drugs and vaccines against COVID-19.
Prevalence and influencing factors of anxiety and depression symptoms among surgical nurses during COVID‐19 pandemic: A large‐scale cross‐sectional study
- Nursing Open
- 752-764
- 10.1002/nop2.1127
Substance misuse prescribing challenges during the pandemic
- Prescriber
- 33-37
- 10.1002/psb.1956
Exclusion and the strategic leadership role of SENCos in England: planning for Covid‐19 and future crises
Commentary on: Is COVID-19 the straw that broke the back of the emergency nursing workforce?
COVID-19 pandemic: end-of-life experience in Australian residential aged care facilities
Regional and sectorial impacts of the Covid‐19 crisis: Evidence from electronic payments
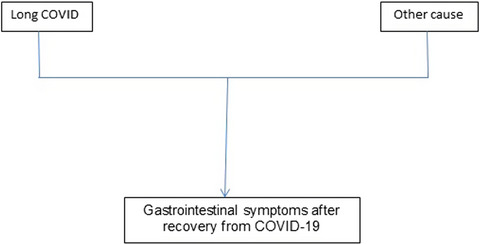
Correspondence on “Prevalence and risk factors for gastrointestinal symptoms after recovery from COVID‐19”
On the interplay of regional mobility, social connectedness and the spread of COVID‐19 in Germany
SARS‐CoV‐2 nucleocapsid protein interacts with immunoregulators and stress granules and phase separates to form liquid droplets
- FEBS Letters
- 2872-2896
- 10.1002/1873-3468.14229
Graphical Abstract

We have identified novel interactors of the SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid (NCAP) protein in human lung epithelial cancer cells. NCAP showed specific interaction with the stress granule (SG) proteins G3BP1, G3BP2, YTHDF3, USP10 and PKR, and translocated to SGs following stress treatments. NCAP exhibited RNA-dependent phase separation. The RNA intercalator mitoxantrone disrupted NCAP assembly in vitro and in cells. This study provides insight into the biological processes and biophysical properties of the NCAP.
Before attributing encephalomyelitis to SARS‐CoV‐2 vaccinations thoroughly exclude differentials
Scalable, methanol-free manufacturing of the SARS-CoV-2 receptor-binding domain in engineered Komagataella phaffii
Graphical Abstract
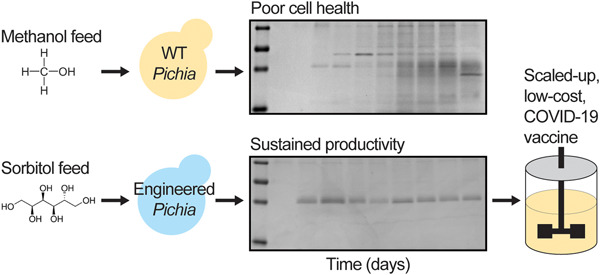
The authors report an improved low-cost manufacturing process in yeast for a component of a clinical-stage COVID-19 vaccine candidate. An engineered strain of Pichia pastoris produces the antigen without using methanol, improving the secreted protein titer and cell health. Elimination of methanol as a process requirement enabled rapid technology transfer to an existing large-scale production facility.
Underlying selection for the diversity of spike protein sequences of SARS-CoV-2
- IUBMB Life
- 213-220
- 10.1002/iub.2577
SARS‐CoV‐2 spike evolutionary behaviors; simulation of N501Y mutation outcomes in terms of immunogenicity and structural characteristic
Socially distanced teaching: The mental health impact of the COVID‐19 pandemic on special education teachers
Dental faculty well‐being amid COVID‐19 in fall 2020: A multi‐site measure of burnout, loneliness, and resilience
Antioxidants associated with NSAIDs might even exacerbate the progress of SARS‐CoV2 disease
- Journal of Medical Virology
- 1264-1266
- 10.1002/jmv.27455
Post‐COVID syndrome symptoms, functional disability, and clinical severity phenotypes in hospitalized and nonhospitalized individuals: A cross‐sectional evaluation from a community COVID rehabilitation service
- Journal of Medical Virology
- 1419-1427
- 10.1002/jmv.27456
Postvaccination SARS‐CoV‐2 infection among healthcare workers: A systematic review and meta‐analysis
- Journal of Medical Virology
- 1428-1441
- 10.1002/jmv.27457
Highlights
-
The overall pooled proportion of COVID-19 infections in partially vaccinated healthcare workers was 2.3%.
-
The overall pooled proportion of COVID-19 infections in fully vaccinated healthcare workers was 1.3%.
-
The overall pooled proportion of COVID-19 infections in unvaccinated healthcare workers was 10.1%.
-
Our findings show decreased incidence of COVID-19 infection as well as decreased incidence of hospitalization, ICU admission and deaths, amongst vaccinated HCWs. There remains an urgent need for healthcare workers to consider getting vaccinated against COVID-19.
Safety and immunogenicity of inactivated COVID‐19 vaccine in health care workers
- Journal of Medical Virology
- 1442-1449
- 10.1002/jmv.27458
Effects of COVID‐19 on a CMOS fabrication course: An integrated design experience
Graphical Abstract
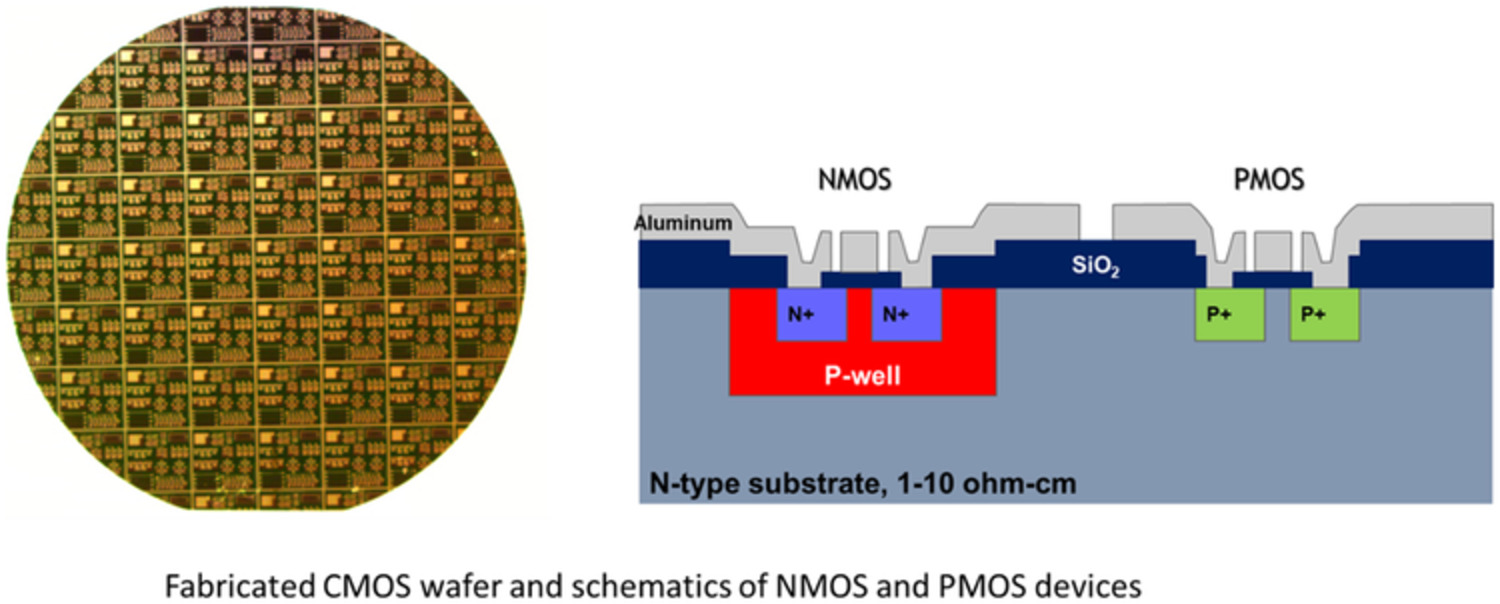
A semiconductor device process design thread is achieved in the course by integrating the laboratory experience and process simulation/modeling and theoretical calculations. The risks associated with the COVID-19 pandemic have forced significant course modifications in both lecture and laboratory components. A remote learning format and video-based laboratory sessions could provide students seamless experiences and learning.
More on CT features in children with COVID‐19
Higher‐dose versus standard‐dose prophylactic anticoagulation in hospitalized patients with COVID‐19
Mandating COVID‐19 vaccination prior to kidney transplantation in the United States: No solutions, only decisions
Graphical Abstract
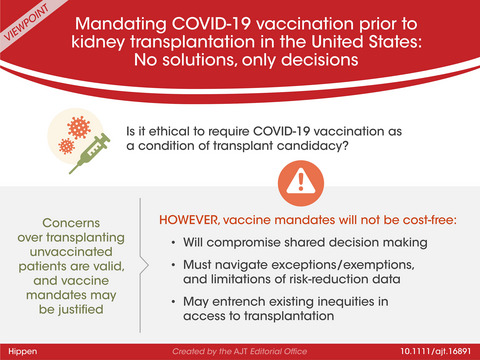
The author discusses the complex ethical issues faced by transplant center leaders in contemplating the institution of a vaccine mandate for actively waitlisted kidney transplant candidates. Silverstein comments on page 335.
What drives people to repost social media messages during the COVID‐19 pandemic? Evidence from the Weibo news microblog
- Growth and Change
- 1609-1626
- 10.1111/grow.12573
Where is community during COVID‐19? The experiences of families living in housing insecurity
Morphea induced by SARS‐CoV‐2 infection: A case report
How COVID‐19 has affected staffing models in intensive care: A qualitative study examining alternative staffing models (SEISMIC)
- Journal of Advanced Nursing
- 1075-1088
- 10.1111/jan.15081
Authors' reply: Hypoalbuminemia in COVID-19
Regarding: Hypoalbuminemia in COVID‐19
Report of two cases of minimal change disease following vaccination for COVID -19
- Nephrology
- 111-112
- 10.1111/nep.13995
Immediate and long‐term effects of the COVID‐19 pandemic and lockdown on physical activity in patients with implanted cardiac devices
Regulatory challenges of convalescent plasma collection during the evolving stages of COVID-19 pandemic in the United States
- Transfusion
- 483-492
- 10.1111/trf.16751
Monotypic plasmacytoid cells mimicking lymph node malignancy in the setting of COVID‐19 recovery
Collaboration in the time of COVID
Asymptomatic COVID‐19 and ST‐elevation myocardial infarction in young adults: lessons learned from two similar cases
- ESC Heart Failure
- 775-781
- 10.1002/ehf2.13690
Healthy eating – a modifiable contributor to optimize healthy living in the COVID‐19 pandemic: a review
SARS-CoV-2 Vaccines and Motor Symptoms in Parkinson's Disease
- Movement Disorders
- 233-233
- 10.1002/mds.28851
A multicenter retrospective study of clinical features, laboratory characteristics, and outcomes of 166 hospitalized children with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID‐19): A preliminary report from Iranian Network for Research in Viral Diseases (INRVD)
Physical activity during the SARS‐CoV‐2 pandemic is linked to better mood and emotion
- Stress and Health
- 490-499
- 10.1002/smi.3111
Face coverings during the pandemic?
Spatiotemporal interactions of a novel mesocarnivore community in an urban environment before and during SARS‐CoV‐2 lockdown
Graphical Abstract
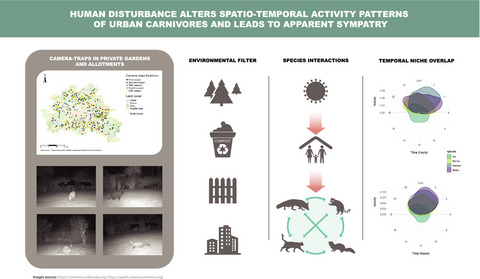
This study contains many dimensions of ecological dynamics: human–wildlife interactions and human activities effects, ecological niche theory, species interactions and community assembly. In an urban environment, mesocarnivores displayed similar spatial requirements, their activities were concentrated during the night and the partitioning appears at a smaller temporal scale.
Broadening the diagnostic approach for SARS-CoV-2 associated myopathy and rhabdomyolysis
COVID‐19 vaccines tolerated in patients with paclitaxel and docetaxel allergy
- Allergy
- 1048-1051
- 10.1111/all.15178
Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation and rehabilitation in patients with COVID‐19: A scoping review
Graphical Abstract

Exercise and rehabilitative activities are increasingly provided in different clinical contexts, not usually considered in the past years. An essential aspect that must be considered when mobilizing patients while on ECMO support is the ineludible necessity to have several professionals available, each taking care of a given part of the treatment, including physiotherapists, nurses, intensive care physicians, perfusionists, ECMO specialists.
Glycated haemoglobin levels among 3295 hospitalized COVID-19 patients, with and without diabetes, and risk of severe infection, admission to an intensive care unit and all-cause mortality
Identifying SARS‐CoV‐2 ‘memory’ NK cells from COVID‐19 convalescent donors for adoptive cell therapy
- Immunology
- 234-249
- 10.1111/imm.13432
Graphical Abstract
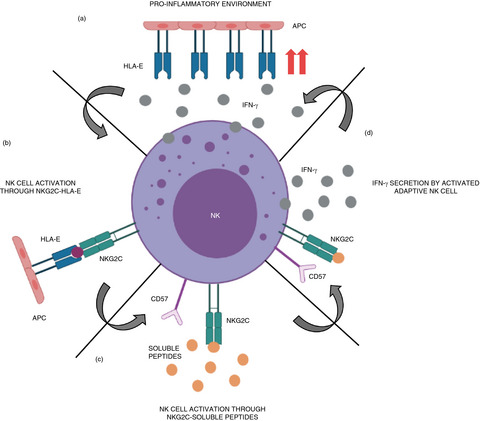
SARS-CoV-2 infection induce a pro-inflammatory environment that could lead to NK cells secreting IFN-γ, increasing HLA-E expression and being activated through NKG2C-HLA-E recognition. The NK cells become adaptive or “memory” cells that can recognize SARS-CoV-2 soluble peptides via NKG2C, triggering a specific inflammatory response to fight this virus.
Whole blood‐based measurement of SARS‐CoV‐2‐specific T cells reveals asymptomatic infection and vaccine immunogenicity in healthy subjects and patients with solid‐organ cancers
- Immunology
- 250-259
- 10.1111/imm.13433
Graphical Abstract
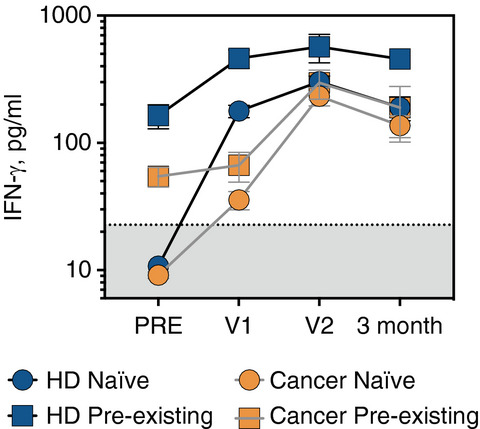
SARS-CoV-2 pandemic continues to cause morbidity and mortality especially in vulnerable patients. Monitoring individuals T and B cell responses to the virus is desirable in high risk populations after infection and/or vaccination. This paper describes a straightforward approach on a small whole blood sample to measure these responses.
COVID‐19 and child marriage: A red flag
Asthma as a risk factor for hospitalization in children with COVID‐19: A nested case‐control study
Dementia in the era of COVID-19. Some considerations and ethical issues
- Psychogeriatrics
- 132-136
- 10.1111/psyg.12773
Evaluation of headache associated with personal protective equipment during COVID‐19
Bullous pemphigoid after SARS‐CoV‐2 vaccination: spike‐protein‐directed immunofluorescence confocal microscopy and T‐cell‐receptor studies
The impact of COVID-19 and political identification on framing bias in an infectious disease experiment: The frame reigns supreme
- Social Science Quarterly
- 2459-2471
- 10.1111/ssqu.13095
Impact of COVID‐19 lockdowns on mental health: Evidence from a quasi‐natural experiment in England and Scotland
- Health Economics
- 284-296
- 10.1002/hec.4453
A qualitative study on a novel peer collaboration care programme during the first COVID‐19 outbreak: A SWOT analysis
- Nursing Open
- 765-774
- 10.1002/nop2.1128
Care in COVID: A qualitative analysis of the impact of COVID‐19 on the health and care of children and young people with severe physical neurodisability and their families
Physiological plausibility of lower viral load in patients with COVID‐19 and olfactory/gustatory dysfunction
Characteristics of hand eczema in final-year apprentice nurses during the COVID-19 pandemic
Graphical Abstract
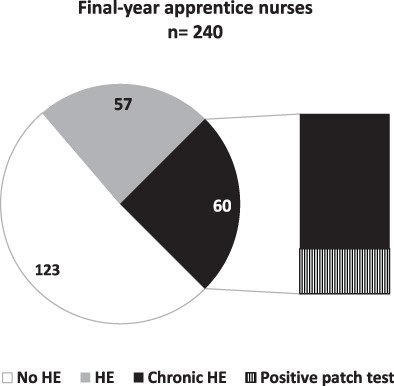
- Clinically observed and self-reported hand eczema were fairly common in final-year apprentice nurses with prevalence of 49% and 46%, respectively.
- Hand eczema was mostly of irritative origin, associated with apprentices’ age and duration of practical training. Contact sensitization was present in 26% of apprentices with chronic hand eczema, rarely to occupational allergens.
- Chronic hand eczema was associated with frequent hand washing and smoking, emphasizing the importance of promoting protective behaviour and lifestyle.
Adapting patient and public involvement in patient‐oriented methods research: Reflections in a Canadian setting during COVID‐19
- Health Expectations
- 477-481
- 10.1111/hex.13387